The polygon is a Layer 2 Blockchain A platform that scales Ethereum by committing checkpoints to the Ethereum mainnet and handling off-chain off-chain before allowing fast and low-cost transactions while maintaining security. The platform serves as a multi-chain ecosystem that addresses Ethereum scalability limitations. Side chain, Plasma Chainand Zero Knowledge Rollup.
What began as a Matic Network in 2017 grew into a giant of blockchain infrastructure. Today, polygon processes 4 million transactions daily across more than 117 million unique wallets. The platform hosts $1.13 billion in tokenized real-world assets across more than 268 issuances, maintaining an average transaction cost of $0.01, with current measured throughput reaching 1,000 transactions per second.
What is a polygon and how does it expand Ethereum?
Polygon is a layer 2 scaling solution that handles off-chain off-chain before committing regular checkpoints to Ethereum mainnet using the Merkle route. This allows faster payments while maintaining Ethereum security guarantees. Unlike Bitcoin Requiring a channel for validity or optimistic rollup of optimism, Lightning networks combine multiple scaling approaches within a unified framework.
Technical foundation supports side chains, plasma chains (first proposed Vitalik Buterin), zero knowledge rollups (such as zksync), and validium implementations (similar to starkex). This multifaceted approach contrasts with single solution competitors, such as the optimistic rollup of Arbitrum and the OP stack implementation of Base.
The platform acts as “”The Internet Value Layer“- A multi-chain infrastructure that rivals the way TCP/IP enables internet communication.
Core Technology Components
Four key components are coordinated to provide a comprehensive scaling infrastructure.
- Polygon POS Chain – EVM Compatible with fast transactions that reflect Ethereum’s smart contract capabilities
- ZKEVM – Zero knowledge proof to improve scalability for implementing snark technology for general calculations
- Miden Rollup – Applications that provide privacy using Starkproof
- Chain Development Kit (CDK) – Allow teams to build custom Layer 2 solutions for application-specific blockchains
Recent upgrades Polygon 2.0 Under a single architectural framework, these previously separate protocols were integrated. The implementation of Agglayer V0.2 and Heimdall V2 reduced transaction finality to 4-6 seconds, reduced block intervals to 2 seconds, and deployed a network of ambitious roadmap targets of 100,000 transactions through the Gigagas Initiative.
How did polygons evolve from their original design?
Polygon conversion from simple sidechains to comprehensive multi-chain ecosystems is one of the most successful pivots of blockchain. The journey spans multiple phases, each marked by the strategic decisions that have shaped today’s platform.
Early development (2017-2020)
The Polygon Journey began in 2017 when Indian developers launched the Matic Network in Mumbai as a plasma-based sidechain. They were implementing the scaling framework originally proposed by Ethereum co-founder Vitalik Buterin and Lightning Network creator Joseph Poon. This project represents one of the first practical implementations of the plasma white paper for Ethereum scaling.
The first mainnet launch in 2020 featured both proof-of-stake and plasma chains designed to handle a variety of transaction types. This approach was similar to Ethereum’s planned sharding strategy before the network pivoted to roll-up-centered scaling. The dual-chain approach provided flexibility, but lacked a unified vision that characterizes modern Layer 2 networks.
Strategic Brands and Expansions (2021-2022)
A significant transformation occurred in February 2021 using a strategic brand from matic to polygons. This change reflects the growing ambition beyond simple sidechains to include multiple scaling solutions such as Zkrollups, optimistic rollups, and interchain protocols.
The strategic acquisition accelerated technical capabilities from 2021 to 2022.
- Acquisition of Hermez Network – $250 million investment to enhance zero knowledge proof capabilities
- Major Funding Rounds – $450 million raised in 2022 to support ambitious development goals
- Starting ZKEVM TESTNET – Practical implementation of proven theoretical scaling solutions
Polygon 2.0 architecture (2023-present)
The introduction of Polygon 2.0 in 2023 represents the most comprehensive architectural evolution since its inception. This upgrade proposed a unified architecture with new port tokens that replace Matic, along with governance reform and technical standardization across all network components.
The implementation accelerated by 2024-2025 with major milestones.
- Launch of the Pol transition – 99.18% completion was achieved on September 4, 2024 by August 2025
- Ecosystem expansion – Growing from 3,000 distributed applications in 2021 to over 120 CDK manufacturing chains by 2025
- Performance improvements – Reduce transaction speed and cost
Who establishes a polygon and what drives that leadership?
The success of a blockchain project ultimately depends on the people behind it. The founding team at Polygon has put together a diverse range of expertise that has proven essential to navigate the complex challenges of building scalable blockchain infrastructure.
Founding Team
Four co-founders founded Polygon, bringing complementary expertise in blockchain engineering, entrepreneurship and product development.
Sandeep Nailwal He is the current CEO of Polygon Labs. He offers his expertise in blockchain programming along with his entrepreneurial experience in founding Health Technology startups. His business development skills have proven important in securing key corporate partnerships that demonstrate institutional trust in the platform.
Jaynti Kanani He served as former CEO and brought deep blockchain engineering experience with special expertise in Ethereum Protocol Development and Web3 Infrastructure.
Anurag Arjun As a former Chief Product Officer, he focused on product management, ensuring technical capabilities to translate into developer-friendly tools and user experiences.
Mihailo Bjelic Information systems engineering expertise is essential for scalable infrastructure design, particularly to address the challenges of multi-chain coordination.
Current organizational structure
The formation of the founding team includes three Indian founders and one Serb founder, reflecting a global perspective from Inception. This international approach has proven advantageous for building relationships across a variety of regulatory environments and market conditions.
The current organizational structure divides responsibility by three professional entities.
- Polygon Lab – Development and technology advancement
- Polygon Foundation – Research, education and governance initiatives
- Polygonal Ecosystem – Grants and Community Development with 1 billion Port Tokens allocated to Community Grants in 2025
Technical leadership includes notable blockchain developers such as Daniel Lubarov, Antoni Martin, Jordi Beirina, Bobbin Thread Bear and Brendan Farmer. This expanded team brings specialized expertise in zero knowledge proof, cryptographic security, and scalable blockchain architectures.
What technology makes polygons different from their competitors?
Polygon’s technology architecture sets it apart from other Layer 2 solutions through several important innovations that address basic blockchain limitations. Rather than focusing on a single scaling approach, the platform combines multiple technologies to create a comprehensive infrastructure solution.
Implementation of zero knowledge proof
Polygon’s technical differentiation focuses on proof of zero knowledge and multi-chain verification capabilities that distinguish it from optimism and single-purpose scaling solutions. Arbitrator. While the platform’s ZK-based solutions can have significantly higher throughput, pessimistic proofs provide an additional layer of security for complex cross-chain operations.
Implementing zero-knowledge proofs extends beyond simple transaction validation, enabling applications that provide complex privacy. The system supports sensitive transactions while maintaining network auditability and addresses regulatory requirements that affect privacy-focused alternatives such as Monero and ZCASH.
Multi-chain verification and staking
The multi-roll ballot system represents a fundamental innovation in blockchain staking economics. Validators are simultaneously piled into different chains within the ecosystem, allowing them to maximize capital efficiency compared to traditional single-chain models.
Pol tokens act as “ultra-production tokens” that serve multiple simultaneous purposes across the ecosystem. Token holders use POL to pay for gas, participate in rewards across multiple chains, and engage in governance decisions.
Agglayer Innovation
Agglomerators represent the most important innovations in polygons to address the challenges of blockchain interoperability. This system acts as a fluidity aggregation protocol that connects multiple chains without the need for trust assumptions between the valiters. This approach differs from traditional bridge protocols that require separate sets of validation devices, instead creating a unified liquidity pool that is accessible across the connected network.
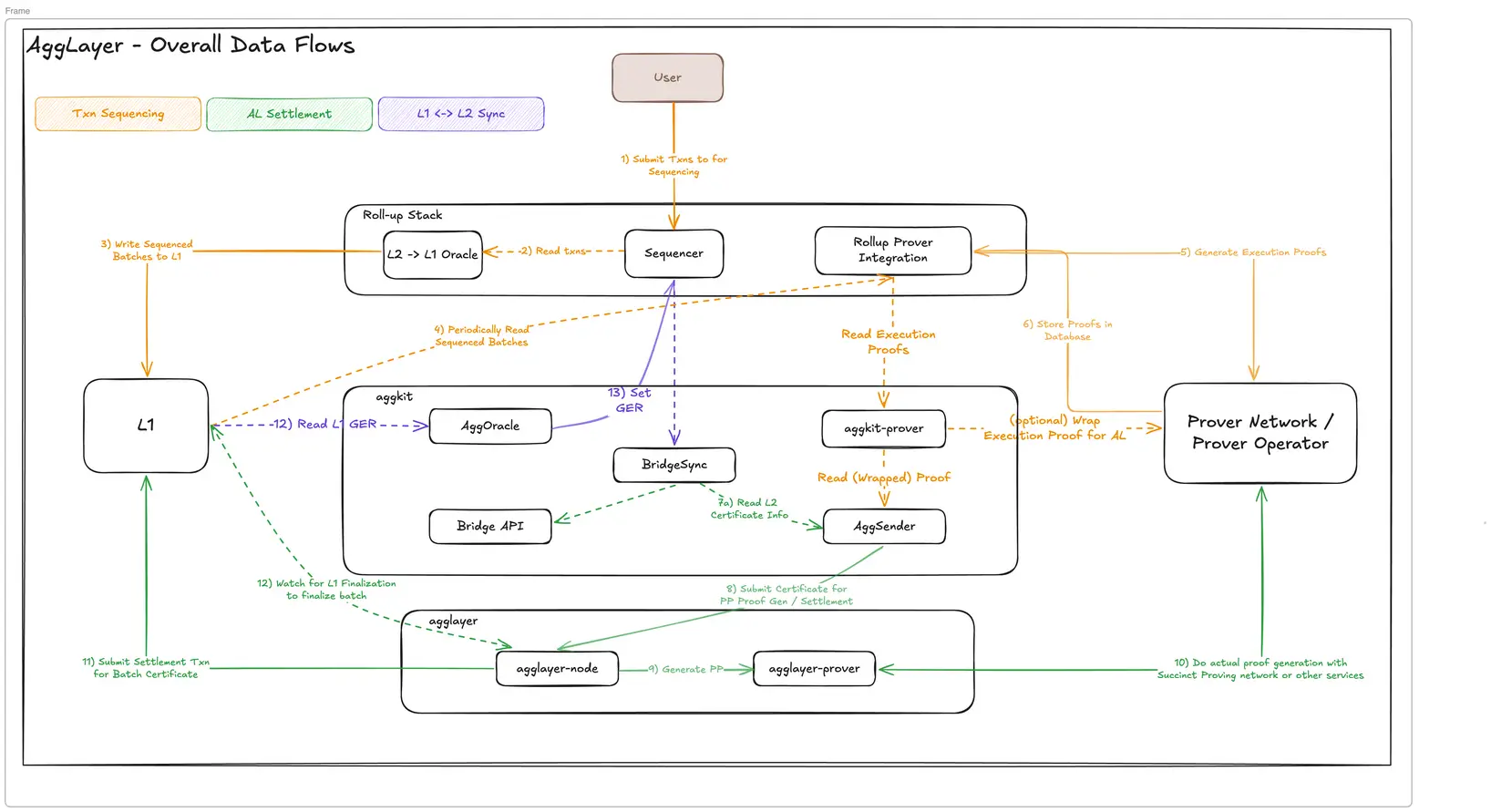
Agglayer Infrastructure Visual (Agglayer Docs)
Privacy and security features
Enhanced privacy and security includes MIDEN’s local execution capabilities for applications that require enhanced confidentiality. Implementation of the EIP-1559 fee market improvements provides more predictable transaction costs compared to simple auction-based systems used in previous blockchain networks.
Advanced encryption technology enables applications that require both transparency and selective privacy, addressing the fundamental blockchain trilemma of scalability, security and decentralization through mathematical proofs, rather than relying solely on economic incentives.
How large is the polygon ecosystem?
The true measure of a blockchain platform is not its technical specifications, but its actual adoption. Polygon’s ecosystem has grown significantly across multiple application categories, showing particular strength in areas that require high transaction throughput and low cost.
Decentralized Finance Applications
The platform currently hosts over 120 chains built using chain development kits. This represents the important adoption of an infrastructure-as-a-service approach.
Decentralized finance Applications lead recruitment metrics and maintain key value with established platforms locked into smart contracts. Polygon’s largest decentralized exchange, QuickSwap holds a total of $398 million (September 2025), but handles thousands of daily transactions at a much lower cost. Underpen At Ethereum MainNet.
Gaming and NFT Platforms
Take advantage of in-game transactions, NFT construction, and gaming applications that include the cost benefits of complex smart contract interactions that can become extremely expensive in Ethereum. Projects such as Decentraland, Sandbox, Aavegotchi show practical blockchain gaming applications that require frequent microtransactions with blockchain ownership guarantees.
The NFT platform benefits from cost-effective mint and trading capabilities that support both individual creators and large-scale commercial operations. The Instagram integration has created 2.5 million wallets, demonstrating mainstream accessibility for users with no prior cryptocurrency experience.
Real-world asset tokenization
Real-world asset tokenization represents the fastest growing application category with assets of $1.13 billion tokenized across more than 268 different issuances. These applications come in multiple asset classes.
- Government securities and local bonds
- Real Estate Investment Vehicles and REITs
- Product support tokens that include gold and agricultural products
- Corporate debt certificates and trade finance
- Infrastructure Project Financing and Green Bond
Corporate and government partnership
Enterprise partnerships demonstrate institutional trust across multiple industries. Meta-integrated polygons Instagram nft Functionality allows millions of users to interact with blockchain technology through the familiar social media interface. Starbucks has implemented loyalty programs using blockchain technology reddit Subreddit Community tokens have been deployed for governance. jpmorgan Built trading applications and Fox Network that leverage Polygon’s infrastructure are used for content delivery. Flipkart’s Integration e-commerce The solution demonstrates practical adoption by traditional business.
Government adoption demonstrates public sector trust in the Philippine budget tokenization project, representing the largest government blockchain implementation to date. The Ministry of Budget Control launched this fully operational system in July 2025, using polygons to notarize and publish key budget documents, including special allocation release orders and notifications of cash allocations. This application illustrates practical use cases for public fund management, transparency, and auditing functions that traditional systems cannot provide.
What is Portochnomics? How do they work?
The economic model of polygons has undergone a radical transformation with the introduction of port tokens. This shift represents more than a simple brand. This established the foundation for multi-chain operations and sustainable ecosystem growth.
Token supply and distribution
$ pol Tokens replaced Matic in 2024, with the cornerstone of the unified Toconamics model of Polygon 2.0. This design supports multi-chain verification and ecosystem expansion.
Unlike Matic’s fixed 10 billion token supply, Pol has an infinite supply mechanism. This allows for the growth of sustainable long-term networks without the constraints of artificial shortages. However, network charges partially burn Pol tokens under certain conditions, creating deflationary pressures that help balance the infinite supply mechanisms during periods of high activity.
Current circulation: As of September 2025, 1.049 billion port tokens
Original matic distribution structure:
- Ecosystem Development Initiative: 23.33%
- Foundation management: 21.86%
- IEO Investor: 19%
- Team Members: 16%
- Reward staking: 12%
- Advisor: 4%
- Private Investors: 3.8%
This represents a more balanced distribution than many projects where teams and early investors hold a majority stake.
Migration Process
The Matic to Pol migration process achieved 99.18% completion by August 2025, maintaining all holder balancing and staking positions through a simple smart contract swap mechanism. This technical achievement demonstrates the network’s ability to perform complex protocol upgrades without disrupting user experience or security.
Multi-chain stake model
The staking mechanism allows the Polholder to protect multiple networks simultaneously, rather than restricting participation to single-chain verification. This implements a similar concept to a shared security model. Multi-roll verification systems create opportunities for higher yields and capital efficiency. Currently, 2.55 billion tokens are trapped in staking.
Governance and Financial Management
The governance framework has evolved from centralized decision-making to community-driven proposals through the Polygon Improvement Proposal (PIP). Token holders participate in protocol decisions, resource allocation, and technical upgrade approvals through a transparent voting mechanism.
Community Financial Management demonstrates and supports practical governance with an allocation of 1 billion port tokens for the 2025 grant.
- Developer Incentives and Recruitment
- Ecosystem Growth Initiative
- Research Projects and Innovation
- Development of public goods
Provides a sustainable funding model for long-term ecosystem development.

1 Billion Port Token Community Grant Program (Polygon.Technolgy)
Economic mechanisms
Protocol emissions provide sustainable incentives for network security through validator rewards, supplemented by additional revenue streams from connected chains of that process Stablecoin transaction. Network charges create deflationary pressure that partially burns Pol tokens under certain conditions and balances an infinite supply mechanism during periods of high activity.
How does Polygon’s governance system work?
Effective Governance It represents one of the biggest challenges of blockchain. Polygon strives to balance the community participation and technical expertise needed to make complex infrastructure decisions.
Proposal and decision-making process
Polygon uses a decentralized governance model to balance community participation with the technical expertise required to determine complex blockchain infrastructure. The system recognizes that blockchain networks require both democratic input and expertise for optimal behavior.
Polygon improvement proposal system Allow community members to suggest changes to protocols, ecosystem improvements, or resource allocation changes. The proposals proceed through a structured review phase, including technical assessments, community discussions, and formal voting processes.
3-pillar governance structure
Includes the 3-pillar governance structure under Polygon 2.0.
- Protocol development – Technical upgrades and infrastructure improvements
- Toconomics – Supply, distribution, and utility decisions
- Community monitoring – Resource allocation and ecosystem direction
Polholders participate in the staking decision and voting process, but technical decisions require additional information from qualified developers and researchers with relevant expertise. This creates checks and balances between different stakeholder groups.
The role of the Ecosystem Council
The Ecosystem Council serves as a professional technical body responsible for smart contract upgrades and protocol security decisions. This structure balances the inputs of a wide range of community with the intensive technical expertise required for complex changes that can affect network security and functionality.
Implementation and safety measures
Implementing governance decisions follows established timelines and procedures designed to prevent rushed changes that could undermine network stability.
- Expanded Discussion Period For upgrading major protocols
- Technical Audit Before implementation
- Step-by-step deployment process Allows thorough testing
Follow best practices established by critical infrastructure projects.
Practical Governance Examples
Community financial management is actually the most visible aspect of governance, demonstrating the system’s ability to make important financial decisions through a collaborative process that incorporates the perspectives of diverse stakeholders. This creates an accountability mechanism for resource allocation decisions.
Validator Governance addresses network security and operational concerns through mechanisms that allow for voter input on technical parameters. These decisions affect block production, transaction processing, network upgrade coordination and require specialized operational knowledge.
Transparency and accountability
Transparency mechanisms make governance decisions and their implementation visible to all stakeholders. Regular reporting, public discussion, and open development processes allow community monitoring of both technology development and resource allocation decisions.
What are the latest developments that shape the orientation of polygons?
The development pace of polygons has accelerated significantly from 2024 to 2025, marking its major technical milestones and increased real-world adoption. These recent developments provide insight into the strategic direction and executive function of the platform.
Upgrading your technology infrastructure
Recent protocol upgrades demonstrate Polygon’s ability to carry out complex technical migrations while maintaining operational continuity. The original POS chain transition to the ZKEVM Validium architecture enhances security properties while maintaining reverse compatibility with existing applications.
Architecture Transition:
- pos to zkevm valium – Improved security properties while maintaining backward compatibility
- Agglayer V0.2 deployment – Reduced transaction finality to 4-6 seconds
- Heimdall V2 implementation – Reduce block interval to 2 seconds to improve user experience
Growth of multi-chain ecosystems
Agglayer adoption has accelerated significantly throughout 2025 with over 120 chains connecting to consolidated liquidity systems. This growth demonstrates market demand for interoperable blockchain infrastructure and examines the strategic focus of polygons on multi-chain adjustment rather than single-chain optimization.
Actual application extensions
Real-world asset tokenization growth exceeded expectations with $1.13 billion assets tokenized across more than 268 issuances by September 2025. This adoption demonstrates institutional trust in the blockchain infrastructure of traditional financial applications.
Asset tokenization Milestones:
- $1.13 billion assets tokenized across more than 268 issuances by September 2025
- Government securities, real estate, goods, and corporate debt certificates
- Institutional trust in blockchain infrastructure for traditional financial applications.
Government and business recruitment
Government blockchain adoption has shown to drive momentum, particularly in budget management and public financial applications. The Philippine Project serves as a success model for other jurisdictions considering the implementation of blockchains for greater transparency and operational efficiency.
The strategic partnership continues to expand with enterprise clients implementing blockchain solutions tailored to specific business requirements. These relationships provide a sustainable revenue stream while demonstrating practical blockchain applications that extend beyond speculative trading or simple token transfers.
Performance and Scalability Roadmap
Gigagas’ roadmap is progressing towards 100,000 transactions per second. It continues through systematic technical optimization and architectural improvements. These developments aim to achieve performance levels comparable to the performance levels of traditional payment processors.
Key development areas include:
- Deploying Zkevm MainNet – Enhanced Zero Knowledge Proof
- Miden Rollout Extension – Applications that provide privacy for specialized use cases
- Performance goals – Aiming for a throughput level comparable to traditional payment processors
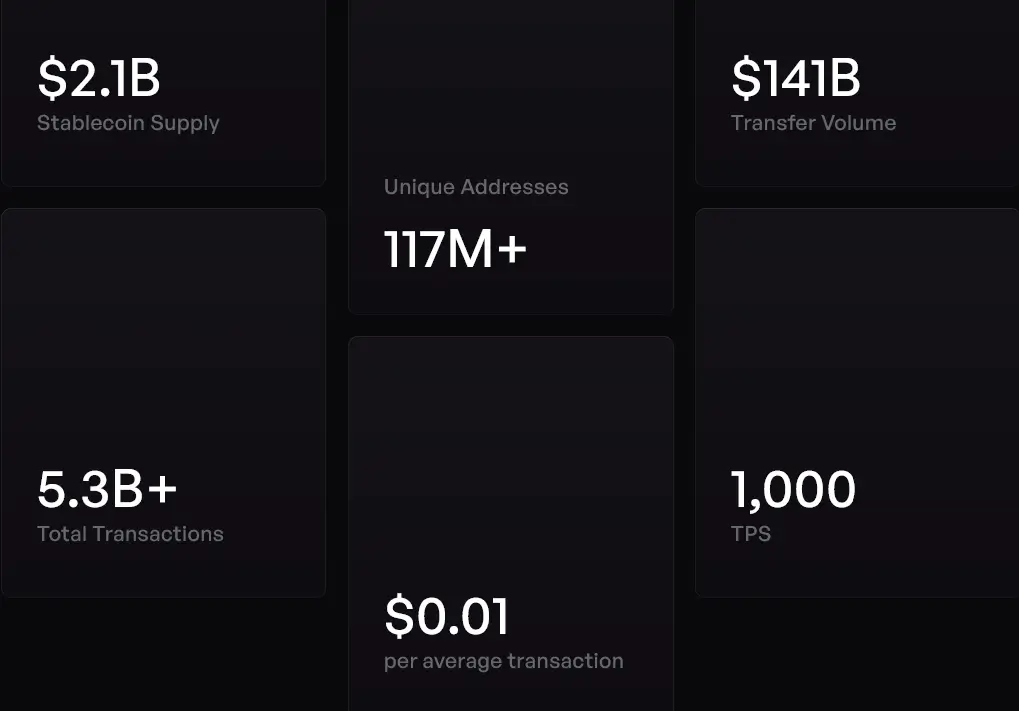
Current Polygon Metric (Polygon.Technology)
What challenges do polygons face in today’s market?
Despite technical achievements and increased adoption, Polygon faces a 2025 reality check. I’ll tell you that the Layer 2 landscape is fiercely competitive, and that the numbers cannot be ignored by polygon leadership.
Competitive pressure indicator
base It appeared as an elephant in the room. Coinbase’s Layer 2 solution leads with a gap that only grows thanks to Polygon’s 21.7 million active addresses with 5.96 million people and Coinbase’s large user base and marketing muscles. Polygon boasts a unique wallet of over 117 million, but the reality is that only fractions, a common pattern across blockchain networks that reveal the difference between hype and persistent engagement, remain actively used.
The locked sum also shows some important observations. Arbitrum has maintained $3.22 billion as of September 2025 compared to Polygon’s $1.2 billion. These aren’t just numbers, they represent actual developers and users’ preferences voting in their wallets.
Performance concerns
Competitive pressures appear in polygon’s own indicators, and trends are not encouraging. Active addresses fell 12% in the first quarter of 2025, but toll revenue fell 38% to $835,000. The weekly decentralized exchange volume fell 20% to $1.2 billion, suggesting that users are moving towards alternatives that provide better liquidity or user experience.
These are important because they create a negative feedback loop. Lower activities means lower fee revenue. This will impact the platform’s ability to fund development and compete with funded rivals.
Technical and operational challenges
Despite ongoing decentralization efforts, concerns about centralization persist.
- Top 10 token holders control about 88% of the supply (mostly smart contracts and exchange wallet addresses)
- Top 5 validators control 47% of the pile poll
- Validator set remains capped with only 100 participants
This creates more centralization than competitors like Ethereum’s proof system.
Technical debt From rapid expansion, it creates its own problems. The platform must support legacy infrastructure while implementing next-generation solutions and enforce difficult trade-offs between backward compatibility and innovation. Resource allocation becomes a zero-sum game when you are trying to maintain the old system while building a new system.
Regulation uncertainty Add another layer of complexity. As governments around the world develop blockchain policies, compliance requirements vary dramatically from jurisdiction to jurisdiction. For global platforms serving diverse markets, this creates an operational headache that smaller, more focused competitors can avoid.
How does Polygon deal with these competitive pressures?
Rather than simply acknowledging the challenges, Polygon has implemented specific strategies to maintain and expand its market position. This approach focuses on technical differentiation and sustainable competitive advantages that competitors cannot easily replicate.
Technical Differentiation Strategies
Polygon’s response to competitive challenges focuses on technical differentiation through the implementation of advanced zero-knowledge proofs and unique, aggregated liquidity solutions that competitors cannot easily replicate.
Agglayer specifically addresses fragmentation concerns by enabling seamless cross-chain liquidity sharing without the need for manual asset bridging. This creates technical advantages through its own infrastructure and ecosystem integration.
Benefits of a competitive core:
- Implementing Agglayer – Seamless cross-chain liquidity sharing without manual asset bridging
- Multi-chain verification – Network effects strengthen as more chains connect to the ecosystem
- Zero knowledge proof – Advanced encryption solutions for scalability and privacy
Multi-chain network effect
Multi-chain verification models create sustainable competitive advantages through network effects that strengthen as more chains connect to the ecosystem. With each additional chain, the validator and user value proposition increases while creating a higher barrier to exit compared to single chain alternatives.
Improved performance and efficiency
Improved protocol efficiency through systematic upgrades demonstrates commitment to technological advances despite market pressure. They provide measurable performance improvements while reducing operational costs for users and developers.
Recent technological achievements include:
- ZKEVM VALIDIUM Transition – Improved security with compatibility
- Heimdall V2 implementation – Reduce transaction speed and cost
- Agglayer Optimization – Improved cross-chain fluidity aggregation
Strategic Market Positioning
Real-world asset tokenization and strategic positioning in government applications create a defensible market niche that requires regulatory compliance and technical reliability. These use cases support an established platform with a proven track record of new alternatives that lack operational history and established regulatory relationships.
This creates the cost of switching enterprise clients through the complexity of compliance certification and integration.
Defensible market niche:
- Real-world asset tokenization – Regulatory compliance and technical reliability requirements
- Government Application – Performance performance and institutional relationship
- Enterprise Partnership – Sustainable revenue from actual utilities rather than speculation
Developers’ Ecosystem Investment
The Community Treasury Department’s grants and the allocation of 1 billion port tokens for ecosystem development creates strong incentives for maintaining developers and attracting new projects. This funding allows for competitive rewards to top developers while supporting innovative projects that may not receive traditional venture capital funds.
This approach implements strategies used by major technology companies to maintain ecosystem leadership.
Community Investment Strategy:
- Allocation of 1 billion Porgrants – Competitive rewards for top developers
- Ecosystem development – Support for innovative projects without traditional VC funding
- Developer Tools – Infrastructure and documentation enhancements
Innovation and research focus
Technological innovation continues through research and development investments in next-generation scaling solutions. GigagRoadmap Advanced encryption implementations position polygons for future market cycles, addressing current performance limitations.
The evolution of governance towards true decentralization addresses concerns about centralization through a systematic redistribution of power and influence. Community Financial Control and Validator Diversification Initiatives work to reduce concentration risk over time.
Conclusion
Polygons grew from experiments Ethereum Sidechain to a multi-chain platform that actually works. The numbers speak for itself: there are 4 million transactions daily across more than 117 million wallets, with an average fee of only one cent. The platform maintains $1.2 billion in locked across the Defi protocol and $1.13 billion in tokenized real-world assets.
The true strength of the platform is not its promise, but its practical applications. Companies like Meta and Starbucks Use it for real world products, like government Philippines It runs a budget system, with the $1.13 billion of traditional assets currently resides in the polygon chain. A successful move from Matic to Portoken reached 99.18% completion, demonstrating that teams can perform complex technical upgrades without compromising stability. It’s not a small feat on blockchain.
Check out the official polygonsWebsite And follow@0xPolygon x for updates.
source:
- Official Polygon Lab Documentation
- Defillama – Polygon Market Data
- COINMARKETCAP – Market and Token Data
- Polygon Foundation – Polygon Community Finance Committee and Governance Framework.
- Philippine Budget Management Office – Blockchain Implementation
- RWA.xyz – Polygon Network Data
- Official Polygon X Account – Recent Updates
- Wikipedia – Polygon
- Agglayer-Document










